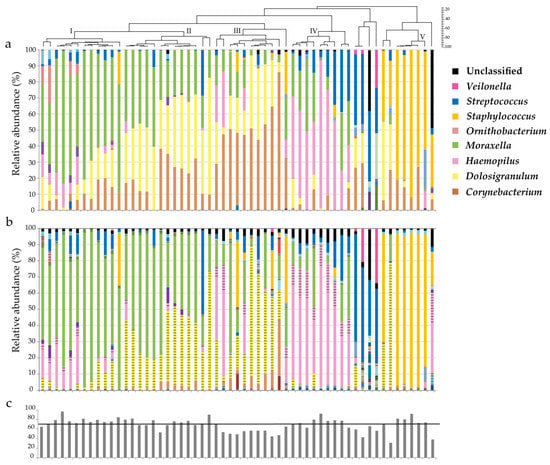
Genes | Free Full-Text | Comparison of Illumina versus Nanopore 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing of the Human Nasal Microbiota
The Application of Nanopore Sequencing Technology to the Study of Dinoflagellates: A Proof of Concept Study for Rapid Sequence-B

Metrichor on Twitter: "NEW @metrichor #epi2me Desktop Agent v3.1.3 Run *MULTIPLE ANALYSES* at the same time! Read about other exciting features in our @nanopore community pages https://t.co/1ujhPy5fY7 https://t.co/7ziKGkPKwM" / Twitter

A computational strategy for rapid on-site 16S metabarcoding with Oxford Nanopore sequencing | bioRxiv
EVALUATION OF THE OXFORD NANOPORE MINION FOR THE IDENTIFICATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF MRSA AND NON- MRSA ISOLATES
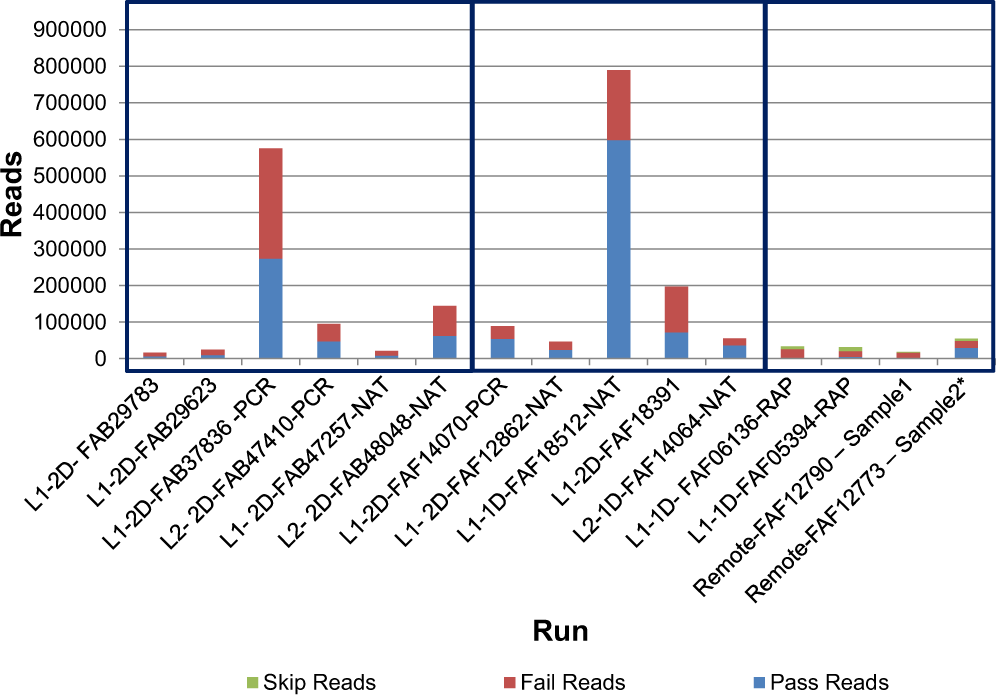
Evaluation of Oxford Nanopore's MinION Sequencing Device for Microbial Whole Genome Sequencing Applications | Scientific Reports

Feasibility of MinION Nanopore Rapid Sequencing in the Detection of Common Diarrhea Pathogens in Fecal Specimen | Analytical Chemistry
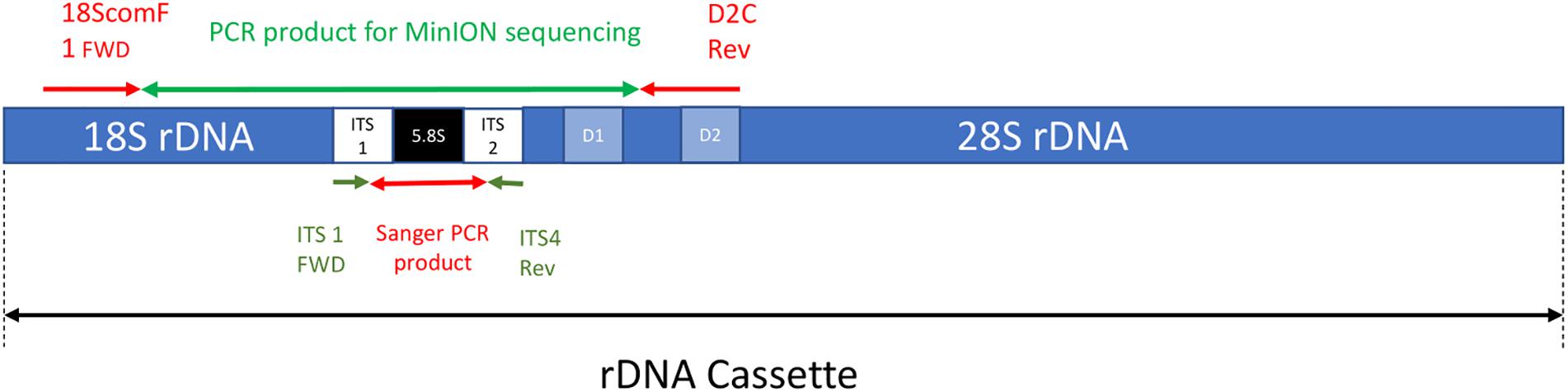
Frontiers | The Application of Nanopore Sequencing Technology to the Study of Dinoflagellates: A Proof of Concept Study for Rapid Sequence-Based Discrimination of Potentially Harmful Algae